Osteoarthritischronic, non-inflammatory disease of the joints or articular cartilage and surrounding tissues. Osteoarthritis is one of the most common diseases, affecting 10-14% of the world’s population. Basically, this disease affects women between the ages of 45 and 55. Osteoarthritis is the most common joint disease and accounts for nearly 80% of all joint etiologies.
The etiology of the disease is currently unknown.. . . Any factor that causes tissue degeneration and aging of the body can lead to the development of this disease, so the onset of osteoarthritis is almost inevitable with advancing age.
External and internal factors also play a role in the development of the disease.The main external factors in osteoarthritis include moisture, hypothermia, unfavorable working conditions, functional overload of the joints with frequent microtraumas, and radiation energy and vibration. The main and fairly common cause of osteoarthritis is that the cartilage cannot withstand the increased strain on the joints. This can be caused by poor posture, long-term work, standing, and even some sports: weightlifting, running, or jumping.
Internal factors that cause the disease include hereditary predisposition to cartilage tissue disease, disruption of blood supply to the joints, hormonal imbalances, and metabolic disorders. Osteoarthritis in women can be caused by ovarian dysfunction during menopause. In addition, vascular processes associated with the early onset of atherosclerosis can cause this disease.
There is also a secondary development of osteoarthritis in diseases such as congenital dislocation, rheumatoid arthritis, intraarticular fractures and even alcoholism.
What are the symptoms and clinical signs of this disease?
Manifestation of osteoarthritis is manifested by severe pain and deformity of the joints, which leads to a violation of their functions. Damage to the load joints (hip and knee joints) and the joints of the hand is the most common cause of this disease. The spine is also involved in the process. But most often, the knee and hip joints are affected.
The most basic symptomin osteoarthritis, severe pain occurs in the affected joints. These pains damage the bones, joints, or periarticular tissues. Typically, such pain increases with effort and decreases at rest. Nocturnal pain, joint swelling, and a feeling of "gel viscosity" in the affected joint in the morning - all indicate the occurrence of osteoarthritis. The intensity of such pain depends on a number of factors (atmospheric pressure, humidity, and temperature changes). All of these factors begin to affect the pressure in the joint cavity that causes these pains.
The next major symptom of osteoarthritis is the cracking or squeaking of the joints, not only while walking, but also during any movement. The appearance of such a crack or squeak is associated with a violation of the joint surfaces, which causes a restriction on mobility in this joint.
In osteoarthritis, there is an increase in the volume of the joints due to the appearance of edema in the periarticular tissues. Swelling or fever in the affected joint is extremely rare.
Clinical forms of osteoarthritis:
- Gonarthrosis.
- Coxarthrosis.
- Osteoarthritis of the distal interphalangeal joints of the hand.
- Osteoarthritis of the proximal interphalangeal joints of the hands.
- Spondylosis deformans.
- Intervertebral osteochondrosis.
GonarthrosisInjury of the knee joint in osteoarthritis. In this case, the pain in the knee joints is expressed while walking and is especially intense when you go down the stairs. The localization of these pains is located in the inner and anterior part of the affected knee joint. The discomfort is increased when the knee is bent. In addition, gonarthrosis in many cases is also a disorder of the knee joint. The disease begins gradually and the pain increases. You can hear crackling with active and passive movements. The pain starts to get worse and in many cases synovitis develops - inflammation of the membrane of the joint or tendon capsule.
Coxarthrosis- This is a change in the hip joint. The initial pain of the hip injury does not appear in the thigh area but in the knee, groin or buttocks. They grow while walking, passing away at rest. These pains, which occur with even minor changes in the x-ray, are accompanied by muscle cramps. With the defeat of the hip joint, the restriction of mobility in the joint gradually increases. This disease is the result of trauma or arthritis. Coxarthrosis is characterized by "duck" gait, lameness, and muscular hypotrophy of the buttocks and thighs. In addition, there is tactile pain in the area of the femoral head.
Osteoarthritis of the distal interphalangeal joints or Heberden nodules of the hand. . . The appearance of such lumps is most commonly observed in women during menopause. They initially appear on the 1st and 3rd fingers of the hand. Over time, namely after a few months or even years, a symmetrical lesion is observed in other distal interphalangeal joints. Such nodules are located on the posterior-lateral surface of the joints.
Osteoarthritis of the proximal interphalangeal joints or Bouchard nodes of the hands. Unlike Heberden's nodules, these nodules appear on the lateral surface of the joint, resulting in lateral enlargement of the joint. Due to this growth, the finger takes on a fusiform shape.
Spondylosis deformans- marginal bone growths appear in the vertebral region as a result of this disease. This disease occurs from the age of 20 years. Osteophytes (bone outgrowths) look like swelling - edema due to compression of the blood vessels. As a result, spinal stiffness appears and in some cases neurological disorders appear.
Intervertebral osteochondrosisoccurs in combination with spinal curvature or deforming spondylosis. In this disease, the disc becomes degenerated and the nucleus extends in different directions, leading to damage to the spine. Overgrowth of osteophytes and an increase in the surface of the joint have also been observed. In this case, the vascular membrane of the joint suffers, resulting in vasculitis - inflammation of the walls of the small blood vessels. Pain syndrome is very pronounced and is exacerbated by physical exertion or hypothermia.
There are two main forms of osteoarthritis- primary or idiopathic (the causes of the disease have not been clarified) and secondary (the disease occurs in the background of other diseases).
Primary osteoarthritislocalizes when less than 3 joints are involved. In localized osteoarthritis, the joints of the spine, hands, and feet, knee joints, hip joints, and other joints are affected.
Generalized osteoarthritis also occurs when 3 or more joints are involved. In this case, the large joints and the distal interphalangeal joints are affected. In addition, erosive osteoarthritis in its generalized form also occurs.
Secondary osteoarthritismay be post-traumatic. In addition, secondary osteoarthritis can be caused by metabolic diseases such as Gaucher disease, which is a genetic disease; Wilson's disease is a rare form of liver damage in which copper metabolism is impaired; Hemochromatosis or, as it is also called, bronchial disease or pigment cirrhosis, is an inherited disease in which the metabolism and accumulation of iron in organs and tissues is violated. Diseases such as diabetes, hypothyroidism - decreased thyroid function, acromegaly - growth hormone hyperactivity can also be causes of osteoarthritis. In addition to these diseases, osteoarthritis can cause calcium deposition disease, neuropathy, and many other diseases.
What happens in osteoarthritis?
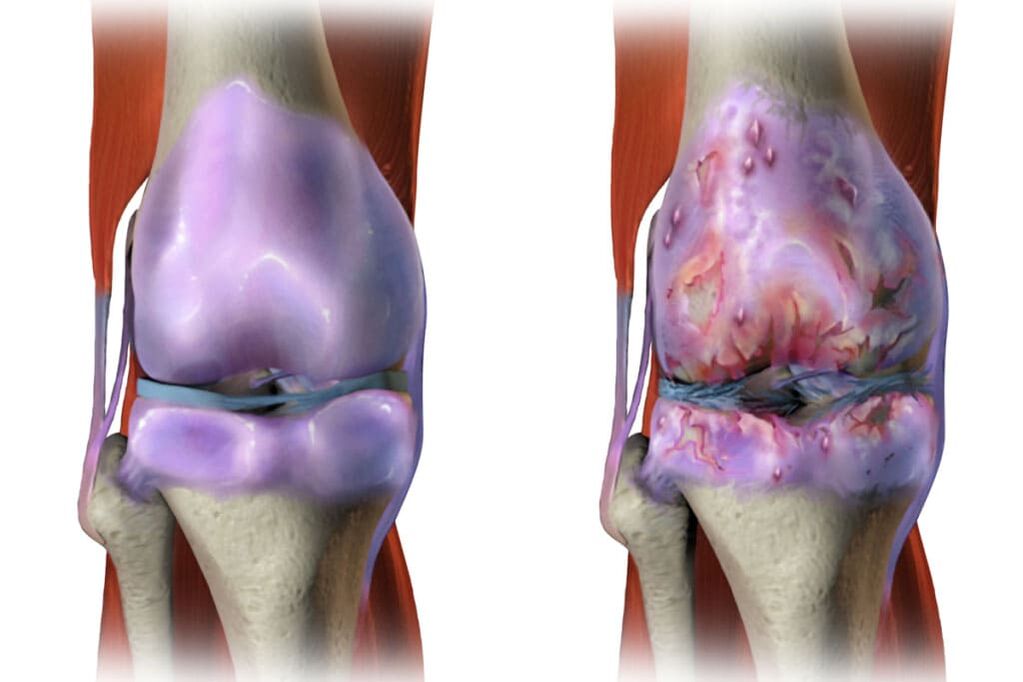
This disease results in intense aging of the articular cartilage. As a result, the elasticity of the articular cartilage decreases. In addition to the roughness of the joint surfaces, cracks still appear on them. In many cases, the cartilage is worn enough to reveal the bone. All this leads to a decrease in the elasticity of the articular cartilage and disturbance of the joints. In addition, inflammation can be associated with all of the listed lesions, resulting in the growth of bone tissue, leading to disease and deformity of the joints.
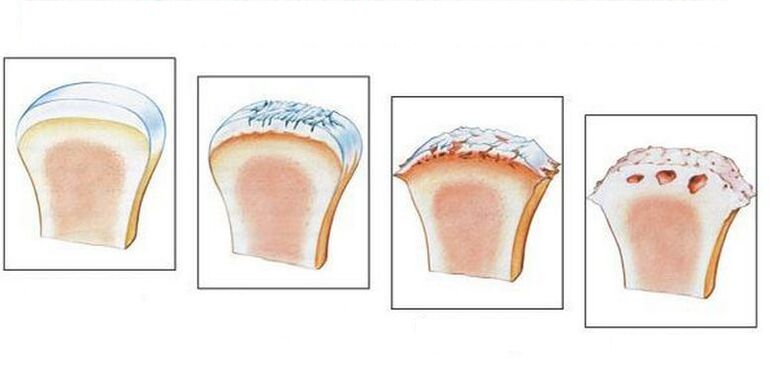
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
The diagnosis of osteoarthritis does not cause much difficulty in many cases. But there are exceptions, such as patients with lesions of the shoulder joint and symptoms of arthritis. Difficulties may also arise in diagnosing primary and secondary osteoarthritis, the occurrence of which is associated with metabolic or other diseases. On X-ray, signs of osteoarthritis are quickly detected (especially in the elderly) if clinical signs of osteoarthritis are present. Insufficient X-ray and laboratory data are available to make a definitive diagnosis. To do this, a number of additional tests are needed to identify the exact cause of the joint pain.
Osteoarthritis treatment
There are both pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods for reducing or completely suppressing pain, which include physiotherapy and practical therapy. An individual approach to each patient is required to prescribe appropriate treatment. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the specifics of the course of the disease.
Above all, the treatment regimen must be followed in the treatment of osteoarthritis, as mechanical strain relief is not only a major factor in pain relief, but also plays an important role in the treatment of this disease. In this case, a relatively long stay in a certain fixed position, prolonged walking and standing on the legs, as well as the exclusion of the transfer of weights, which could lead to mechanical overload of the joints, must be ruled out. If the disease is neglected, the patient is advised to walk on a crutch or stick. Some patients require a half-bed system for pain that is quite pronounced at the time the disease gets worse.
A diet to reduce overweight is recommended when treating osteoarthritis. This is especially true for those with lesions of the knee joints.
In addition, physiotherapeutic methods are used to treat the disease, which not only reduce pain and inflammation, but also have a positive effect on the metabolic processes of joint tissues and improve microcirculation. Physiotherapy treatments include electric current, alternating magnetic current, electrophoresis, and ultraviolet radiation and phonophoresis at the affected joints. In addition, thermal processes and the use of peat sludge and paraffin wax are prescribed.
Using the elements of therapeutic massage, patients should try to avoid mechanical irritation of the joint capsule. Only in this case does the painful muscle spasm decrease and the tone of the weakened muscles also increases, as a result of which the patient's functional abilities improve.
Medication is prescribed depending on the form of the disease and the severity of its course. In more severe cases, patients are prescribed surgery (arthroplasty).
In addition, patients are advised to resort to seafront spa treatments.
Prevention of osteoarthritisit consists of performing special exercises on a daily basis that help strengthen the muscles and tendons. Getting rid of excess weight, restricting weight carrying, and including foods such as jelly, jelly, or aspen on the menu are all measures to prevent osteoarthritis. And of course in sports like swimming. It should be remembered that it is better to prevent all diseases than to cure them. The same goes for diseases like osteoarthritis. In order not to think about how to get rid of severe pain in osteoarthritis in the future and how to cure this disease, preventive measures must be taken today without being postponed.
Treatment of deforming osteoarthritis by various methods
The high level of education and experience gained in the use of shock wave therapy makes it possible to achieve the maximum positive effect of the treatment even in the advanced stage of the disease, in many cases avoiding the surgical treatment.
Shockwave therapy is performed on a modern device:

- the process of treating arthritis with the UHT method consists of 5-7 sessions;
- the meeting will be held once within 5-7 days.
The shock wave loosens the microcrystals of calcium salts in the affected tissues and the fibrous areas that form in the tissues of the joints. At the same time, blood flow in damaged tissue increases tenfold, contributing to the absorption of calcium salts and fibrous areas.
Advantages of the SWT method:
- efficiency;
- good tolerance (does not require anesthesia);
- reduces the need for other methods, especially surgical treatment;
- rapid pain relief without analgesics;
- the potential for use in the chronic phase of the disease and its primary manifestations;
- performed on an outpatient basis, does not require hospitalization, does not interfere with the patient’s normal rhythm of life.
Photodynamic therapy in orthopedicsNon-invasive, uncomplicated, two-component treatment method. The method uses a photosensitizer and a laser beam source with a wavelength of 660-670 nm approved for medical use.
Under the influence of the laser beam, a photosensitizer is excited by the release of singlet oxygen, which is toxic to the energy complexes of the cell (mitochondria and the Golgi complex), destroying the latter and thus initiating the irreversible process of apoptosis. However, healthy cells are not damaged. Damaged abnormal tissue is absorbed aseptically.
The photosensitizer is injected transcutaneously (applications) into the patient's body.
PRP plasma lifting- This orthopedic procedure is based on a patented method of processing a patient's blood using special vacuum biotechnology tubes and a special centrifugation method.
In the method, an injection form of autoplasma containing platelets is isolated from the patient's blood and injected into the soft tissues surrounding the joint and directly into the patient's joint cavity. Autoplasma injections can reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and restore range of motion in the joint. The autoplasma treatment procedure minimizes or eliminates the number of drugs used, thereby reducing the toxic effects of the drugs on the patient's body. In addition, autoplasma injections help to reduce treatment times by a factor of 2-3.
Indications for the procedure (PRP plasmolifting):
- osteoarthritis;
- osteoarthritis;
- periarthritis;
- tendon diseases,
- damage to ligaments and muscles.
Thus, in orthopedics, shock wave therapy, photodynamic therapy, and plasma lifting (PRP) are the best choices for treating joint disease. They use modern equipment and technologies, as well as the experience of doctors, to achieve positive results.


















































